Toja Grid Lean-To A Comprehensive Guide
Toja grid lean to – Toja grid lean-to structures offer a practical and adaptable solution for various needs. This guide delves into the intricacies of design, construction, and application, exploring the possibilities and considerations involved in building one. From understanding the fundamental aspects of a toja grid lean-to’s definition and construction methods to analyzing its applications and environmental impact, we’ll explore all facets of this versatile structure.
The detailed explanation encompasses various aspects, including possible designs, materials used, sizes, pros and cons, construction steps, anchoring methods, structural integrity, fastening techniques, tools needed, common uses, adaptability to different climates, comparisons with similar structures, design factors, ventilation, water resistance, roof designs, material costs and substitutes, durability, maintenance requirements, repair procedures, preventative measures, common issues and solutions, environmental impact, sustainable materials, waste minimization methods, and potential ecological benefits. A comprehensive table summarizing key information will further aid in understanding.
Definition and Description
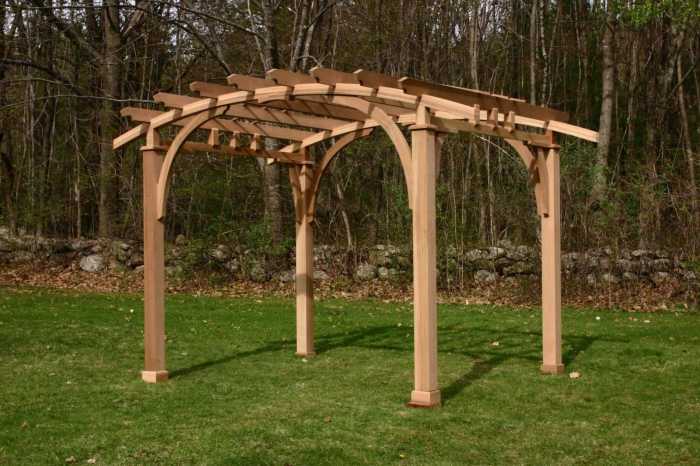
A toja grid lean-to is a type of temporary or semi-permanent shelter, often used for outdoor activities, construction sites, or as a basic living space. It leverages a grid-like framework, typically made of lightweight yet durable materials, for supporting the sloping roof. This structure offers a defined space with shelter from the elements, without the complexity and cost of a traditional building.
The design facilitates easy assembly and disassembly, making it adaptable to various needs and locations. Its lightweight nature allows for transportation and relocation if necessary, making it ideal for temporary or mobile use cases.
Possible Designs and Configurations
Different toja grid lean-to designs cater to various needs and preferences. Some designs feature a simple gable roof, while others might employ a more complex, multi-pitched roof system. Variations in the grid framework’s dimensions and spacing can accommodate different sizes and shapes of the lean-to. The grid structure’s angle, relative to the ground, dictates the amount of space and the overall volume of the shelter. Some designs include integrated features like windows or doors, depending on the intended use and climate.
Materials Commonly Used
Common materials used in constructing toja grid lean-tos include lightweight wood, such as treated lumber or pressure-treated plywood. Aluminum or steel frames are also prevalent choices, providing robust support and resisting corrosion. The roofing material is typically made of waterproof and weather-resistant materials, such as polyethylene sheeting, corrugated plastic, or canvas. The selection of materials directly impacts the overall cost, durability, and weather resistance of the structure.
Sizes and Dimensions
The size and dimensions of a toja grid lean-to are highly customizable. They can range from small structures, perfect for a single person, to larger ones suitable for groups or as a small workshop. Sizes are often determined by the specific application, ranging from approximately 10 square feet to 100 square feet or more. Factors such as the number of people needing shelter and the intended purpose influence the required dimensions. Detailed plans and blueprints can be used to ensure the lean-to meets specific space requirements.
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Easy assembly and disassembly | Potential for weaker structural integrity compared to traditional structures. |
| Lightweight and portable | May require additional reinforcement for strong winds or heavy snow |
| Relatively inexpensive to construct | Limited insulation compared to permanent buildings |
| Adaptable to various sites and uses | Potential for leaks if materials are not properly installed or maintained |
| Fast construction time | May require additional waterproofing measures in harsh climates |
The table above highlights the advantages and disadvantages of utilizing a toja grid lean-to. Weighing these factors is crucial for determining their suitability for a specific project.
Construction Methods
Constructing a Toja grid lean-to involves a methodical approach to ensure structural integrity and longevity. Careful consideration of materials, anchoring, and fastening techniques is paramount for a stable and functional structure. The following sections detail the step-by-step process and critical considerations for building a Toja grid lean-to.
Step-by-Step Construction Process
The construction of a Toja grid lean-to typically follows a phased approach, beginning with the foundation and progressing to the roof and finishing touches. Initial preparation involves site assessment, material gathering, and layout planning. Precise measurements and markings are essential for accurate assembly. The framework is constructed using the Toja grid system, with careful attention to ensuring proper alignment and support. Subsequent steps include installing the roofing material, ensuring proper ventilation and drainage, and finally completing any finishing details.
Anchoring Methods
Appropriate anchoring methods are crucial for the structural stability of a Toja grid lean-to. Various anchoring methods can be employed, each with its specific advantages and considerations. These methods include using ground anchors, buried metal plates, or strategically placed concrete footings. Ground anchors are often used for temporary structures, while buried metal plates or concrete footings are suitable for more permanent installations. The choice of anchoring method depends on factors like soil conditions, anticipated loads, and the intended lifespan of the structure.
Ensuring Structural Integrity
Structural integrity in a Toja grid lean-to is achieved through meticulous attention to detail throughout the construction process. Correct alignment of the Toja grid components is essential, as is using appropriate fasteners. Regular checks and adjustments during construction are critical for maintaining the intended geometry. Additionally, ensuring adequate support for the roof load is paramount. This includes using the correct roofing material and appropriate supporting beams.
Fastening Methods
Fastening methods used in Toja grid lean-to construction significantly impact the structural integrity and longevity of the structure. Appropriate fasteners must be chosen based on the materials used and the load they will need to bear. Using high-strength, weather-resistant fasteners is critical for the structure’s long-term performance. Examples include using galvanized screws for metal connections and using appropriate fasteners for joining wood components.
Tools Needed for Construction
Accurate and efficient construction requires the proper selection and use of tools. The following table lists the essential tools needed for building a Toja grid lean-to.
| Tool Category | Specific Tools |
|---|---|
| Measuring and Marking | Measuring tape, level, pencil, marker, spirit level |
| Cutting and Shaping | Hand saw, power saw (if needed), drill, screwdriver |
| Fastening | Screwdrivers, drill, hammer, nails (if applicable), bolts, nuts, washers |
| Support and Handling | Safety glasses, gloves, work boots, work apron |
| Finishing | Caulk gun, sealant, paint (if applicable) |
Applications and Uses
Toja grid lean-tos offer a versatile and adaptable solution for various construction needs. Their lightweight nature and modular design make them suitable for temporary structures as well as more permanent installations. This flexibility extends to diverse climatic conditions and geographical locations.
The adaptability of the toja grid lean-tos stems from their simple yet robust design. The grid system allows for customized configurations, facilitating a wide range of applications, from temporary shelters to more permanent structures. Furthermore, the material selection options allow for diverse aesthetic choices and durability, accommodating different budgetary considerations.
Common Uses
Toja grid lean-tos find widespread use in various contexts. Their utility extends beyond simple temporary shelters, making them suitable for a variety of projects. Their ease of assembly and cost-effectiveness make them attractive for construction sites, events, and residential settings.
- Temporary housing for construction workers provides basic shelter and protection from the elements.
- Emergency shelters in disaster-prone areas, effective and efficient solutions for temporary accommodation.
- Agricultural structures, such as animal shelters or temporary storage facilities for crops, offer practical and cost-effective solutions.
- Event spaces provide flexible and adaptable spaces for various gatherings, like festivals or concerts.
- Outdoor classrooms or workshops offer an easily erected and modifiable space for educational or training purposes.
Potential Applications in Different Settings
The versatility of the toja grid lean-to extends to diverse settings, making it a valuable option for various projects. The adaptability of the structure allows it to integrate seamlessly into different environments.
- Residential Settings: Toja grid lean-tos can be used as extensions to existing homes, creating additional living space or outdoor rooms, like a sunroom or a covered patio.
- Commercial Settings: Businesses can use toja grid lean-tos as temporary offices, storage areas, or sales booths at trade shows and markets.
- Recreational Settings: The structure is ideal for creating shaded areas in parks, camping grounds, or recreational areas, offering protection from the sun or rain.
Adaptability for Various Climates
The toja grid lean-to design can be adjusted to suit different climatic conditions. The material choice and structural configuration are crucial factors in achieving this adaptability.
- Warm Climates: Open designs and lightweight materials are preferable in warm climates, promoting airflow and reducing heat buildup. This includes the use of breathable fabrics or lighter-colored materials for the roofing and walls.
- Cold Climates: Insulation and materials that resist cold weather are important considerations. Double-layered walls, insulated roofing, and appropriate thermal barriers can help retain heat.
Comparison with Other Similar Structures
Compared to other similar structures, the toja grid lean-to stands out for its ease of assembly, adaptability, and cost-effectiveness.
- Traditional Lean-tos: Toja grid lean-tos are significantly faster and easier to erect than traditional lean-tos, due to their prefabricated components and modular design.
- Prefabricated Cabins: Toja grid lean-tos are more economical and adaptable than prefabricated cabins for temporary needs. They are lighter and more easily transported, offering greater flexibility in location.
Scenarios for Beneficial Use
The table below highlights various scenarios where a toja grid lean-to can provide a practical and cost-effective solution.
| Scenario | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Temporary housing for construction workers | Provides basic shelter, reduces construction costs, and improves worker morale. |
| Disaster relief shelters | Rapid deployment, low cost, and easy assembly enable quick response in emergencies. |
| Agricultural storage | Cost-effective solution for temporary crop storage or animal housing. |
| Outdoor events | Provides a flexible and adaptable space for various events, reducing setup and teardown time. |
Design Considerations
Designing a Toja grid lean-to requires careful consideration of several factors to ensure structural integrity, functionality, and aesthetic appeal. A well-designed lean-to will withstand various weather conditions and provide a useful space for its intended purpose. Proper planning and attention to detail are crucial for achieving a durable and satisfactory outcome.
The primary design considerations encompass structural stability, ventilation, water resistance, and aesthetic choices. The following sections will delve into each of these critical elements, highlighting their importance in the overall design process.
Structural Stability
Toja grid lean-tos, due to their open framework, demand meticulous attention to structural stability. This involves careful selection and placement of support posts, ensuring adequate bracing and appropriate grid dimensions. The weight-bearing capacity of the materials must be carefully assessed to accommodate anticipated loads, such as snow accumulation and wind pressure. Appropriate connections and joints are crucial to prevent any potential structural failure.
Ventilation
Adequate ventilation is paramount for a comfortable and healthy indoor environment. Poor ventilation can lead to moisture buildup, mildew, and potentially mold. The design should incorporate features that allow for natural airflow, such as strategically placed openings and gaps. Consider the prevailing wind direction and ensure that the openings are not blocked by obstructions. In addition, consideration of passive ventilation techniques will enhance the overall performance of the structure.
Water Resistance
Water resistance is critical for the longevity and functionality of a Toja grid lean-to. The design should incorporate measures to prevent water from penetrating the structure. This involves selecting waterproof or water-resistant materials for the roof and walls, along with proper sealing of joints and seams. The slope of the roof and the overhang are critical in directing rainwater away from the structure. The use of appropriate coatings and sealants will greatly increase the resistance of the structure to moisture damage.
Roof Designs
Various roof designs can be employed for a Toja grid lean-to, each with its advantages and disadvantages. A simple sloping roof is straightforward to construct, while a more complex design, such as a gabled roof, may offer improved protection from the elements. A hip roof, with its sloped surfaces meeting at the peak, provides excellent water shedding capabilities. Consideration of the local climate and the desired aesthetic will greatly influence the choice of roof design.
- Simple Sloping Roof: A simple sloping roof design is often preferred for its ease of construction. The roof angle is crucial for effective water runoff, minimizing the risk of water damage to the structure. The angle should be carefully calculated to ensure proper drainage.
- Gabled Roof: A gabled roof, characterized by sloping sides meeting at a ridge, offers enhanced protection against the elements compared to a simple sloping roof. The design increases the overall area covered by the roof, providing a larger sheltered space. The design is generally more complex and may require more materials.
- Hip Roof: A hip roof, featuring sloping sides meeting at a ridge and sloping edges that connect to the ground, is known for its exceptional water shedding capabilities. The design minimizes the risk of water pooling and offers comprehensive protection. The construction process can be more complex and labor-intensive compared to simpler designs.
Design Summary Table
| Design Aspect | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Structural Stability | Material strength, support post placement, bracing, connections, and anticipated loads (snow, wind). |
| Ventilation | Strategic openings, prevailing wind direction, and passive ventilation techniques. |
| Water Resistance | Waterproof/water-resistant materials, proper sealing, roof slope, and overhang. |
| Roof Design | Simple sloping, gabled, hip – based on local climate and aesthetics. |
Materials and Cost Analysis
Toja grid lean-tos offer a versatile and cost-effective solution for various applications. A crucial aspect of this construction type is understanding the material costs and their impact on the overall project budget. This section delves into the typical costs, potential substitutes, durability, and cost-benefit analysis of different materials commonly used in toja grid lean-tos.
Typical Material Costs
Material costs for a toja grid lean-to vary significantly based on the chosen materials, local market prices, and the size of the structure. Generally, framing materials like treated lumber, steel, or aluminum, along with roofing materials like asphalt shingles or metal sheeting, constitute the bulk of the cost. Installation labor and permitting fees will also add to the total project expense.
Potential Material Substitutes
Exploring alternative materials can often lead to cost savings without compromising structural integrity or aesthetic appeal. Recycled or reclaimed lumber, for instance, can significantly reduce costs while aligning with sustainability goals. Using composite materials for sheathing or siding can also offer better water resistance and reduced maintenance. Consideration should be given to the availability and suitability of local resources, which might include locally sourced bamboo or other regionally appropriate materials.
Durability and Longevity of Common Materials
The longevity of a toja grid lean-to hinges on the durability of the chosen materials. Pressure-treated lumber, a common choice for framing, offers good resistance to rot and insect damage, extending the structure’s lifespan. Metal roofing, such as galvanized steel, exhibits excellent durability and longevity, providing long-term weather resistance. However, factors like proper installation, regular maintenance, and the environmental conditions play a critical role in the actual lifespan of the structure.
Cost and Benefit Comparison
The optimal material choice balances cost-effectiveness with desired durability and longevity. While treated lumber might be more affordable initially, its potential long-term maintenance requirements need to be considered. Metal roofing, while higher upfront, often translates to lower long-term maintenance and replacement costs. Assessing the specific environmental conditions and anticipated lifespan of the structure is essential for making an informed decision.
Estimated Material Costs
| Lean-to Size (sq ft) | Estimated Cost (USD) – Framing | Estimated Cost (USD) – Roofing | Estimated Cost (USD) – Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | $1,500 – $2,500 | $1,000 – $1,500 | $2,500 – $4,000 |
| 150 | $2,250 – $3,750 | $1,500 – $2,250 | $3,750 – $6,000 |
| 200 | $3,000 – $5,000 | $2,000 – $3,000 | $5,000 – $8,000 |
Note: These are estimated costs and can vary based on location, material quality, and labor rates.
Maintenance and Repair
Maintaining a Toja grid lean-to requires a proactive approach to prevent costly repairs and ensure its longevity. Regular inspections and timely maintenance are crucial for preserving the structure’s integrity and aesthetic appeal. This section details the specific maintenance requirements, repair procedures, and preventative measures for a Toja grid lean-to.
Maintenance Requirements
Regular maintenance is essential to prevent the deterioration of materials and the development of structural issues in a Toja grid lean-to. This involves visual inspections, cleaning, and addressing minor issues promptly. Failure to adhere to these procedures can lead to increased repair costs and potential safety hazards.
- Visual Inspections: Conduct regular visual inspections of the entire structure, including the frame, cladding, and fasteners. Look for signs of damage, such as cracks, rust, or loose components. Early detection and resolution of minor issues are key to preventing larger problems.
- Cleaning: Regular cleaning of the cladding and frame is crucial for maintaining the aesthetic appeal and preventing the buildup of dirt, debris, and moisture, which can accelerate corrosion and decay.
- Fastener Check: Periodically check all fasteners for tightness and securement. Loose fasteners can compromise the structure’s integrity and lead to eventual damage. Tighten or replace as necessary.
Repair Procedures
Proper repair procedures are vital for restoring a Toja grid lean-to to its original condition. Following these procedures minimizes the risk of further damage and ensures structural integrity.
- Minor Damage Repair: Address small cracks or loose fasteners promptly. Use appropriate fasteners, adhesives, or sealants to restore the affected areas to their original condition.
- Structural Damage Repair: For more significant damage, such as structural cracks or bent supports, consult a qualified structural engineer for a proper assessment and repair plan. Incorrect repairs can compromise the stability of the lean-to.
- Cladding Repair: If the cladding shows signs of damage or deterioration, replace the damaged sections with identical materials to maintain the aesthetic uniformity. Using different materials might compromise the design intent.
Preventative Measures
Proactive measures are essential for extending the lifespan of a Toja grid lean-to. This includes proper installation, material selection, and consistent maintenance.
- Proper Installation: Ensure the lean-to is installed according to the manufacturer’s specifications. This foundational step is vital for preventing future issues.
- Material Selection: Choose high-quality materials that are resistant to the local climate conditions (e.g., weatherproofing, UV resistance). This choice ensures long-term durability.
- Regular Maintenance Schedule: Implementing a regular maintenance schedule (e.g., quarterly or semi-annually) will significantly improve the lifespan of the structure and help catch potential issues early.
Common Issues and Solutions
Identifying and addressing common issues in a Toja grid lean-to is crucial for preventing further damage.
- Rust: Rust is a common issue for metal components. Apply rust-proofing paint or coatings to prevent further corrosion.
- Water Damage: Water penetration can lead to rot and structural weakening. Ensure proper drainage around the lean-to and address any leaks promptly.
- Loose Fasteners: Regular checks for loose fasteners are vital. Tighten or replace loose fasteners to maintain structural integrity.
Maintenance Schedules and Repair Procedures
The following table provides a sample maintenance schedule and corresponding repair procedures for a Toja grid lean-to. This is a general guideline, and specific schedules should be tailored to the specific environment and use of the lean-to.
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Repair Procedure |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Monthly | Inspect for cracks, rust, or loose fasteners. |
| Cleaning | Quarterly | Clean cladding and frame. |
| Fastener Check | Semi-annually | Check all fasteners for tightness. |
| Cladding Inspection | Annually | Inspect for damage or deterioration. |
| Structural Inspection | Annually | Inspect for structural integrity. Consult the engineer if necessary. |
Environmental Impact: Toja Grid Lean To
Toja grid lean-tos, with their inherent structural flexibility and potential for customization, offer a range of environmental implications. Careful consideration of materials, construction methods, and design choices is crucial to minimizing their overall impact on the surrounding ecosystem. The selection of sustainable materials and efficient construction techniques can substantially reduce the carbon footprint associated with these structures.
A thoughtful approach to environmental impact assessment can guide the design and construction of toja grid lean-tos, leading to structures that are both functional and environmentally responsible.
Material Selection for Sustainability
Sustainable materials significantly reduce the environmental footprint of a toja grid lean-to. Choosing materials with low embodied energy, recycled content, and renewable sources minimizes the impact on natural resources. Examples include using reclaimed lumber for framing or bamboo for sheathing. Local sourcing of materials reduces transportation emissions and supports regional economies.
Waste Minimization Strategies
Minimizing waste during construction is crucial for environmental responsibility. Detailed pre-construction planning, precise material measurements, and the use of scrap-reducing techniques are key. Proper disposal of construction waste, including recycling and composting, further reduces environmental impact. Construction teams should prioritize waste reduction and reuse strategies.
Ecological Benefits
Properly designed toja grid lean-tos can contribute to ecological benefits. For example, the use of native plants for landscaping can support local biodiversity and reduce the need for water-intensive species. Sustainable design principles can promote habitat creation, reducing the impact of the structure on the existing ecosystem.
Comparative Environmental Footprint Analysis, Toja grid lean to
A table comparing the environmental footprint of different toja grid lean-to designs provides a valuable tool for informed decision-making. This analysis considers factors like material sourcing, construction methods, and energy use. This allows for comparison across various designs, optimizing the structure for a reduced environmental impact.
| Design Feature | Design A (Conventional) | Design B (Sustainable) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Sourcing | Regional, but with some imported components | Predominantly locally sourced, recycled, and renewable |
| Construction Waste | A significant amount of waste is generated | Minimized waste through pre-planning and reuse |
| Energy Consumption (Construction) | High energy use from transportation and machinery | Lower energy use due to local sourcing and efficient techniques |
| Carbon Footprint (estimated) | High | Low |
| Biodiversity Impact (estimated) | Potential negative impact due to habitat loss | Potential positive impact due to habitat enhancement |
Closure
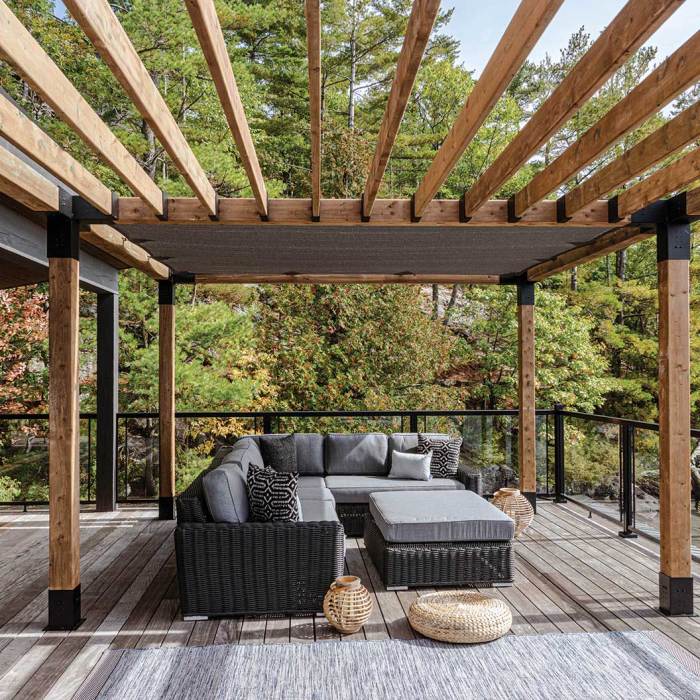

Source: com.au
In conclusion, the toja grid lean-to presents a robust and adaptable structure suitable for diverse applications. Careful consideration of design factors, material choices, and construction methods ensures a sturdy and long-lasting structure. Understanding the maintenance requirements and environmental impact allows for responsible construction and use. This comprehensive guide provides a framework for anyone looking to build, use, or learn more about this unique structure.